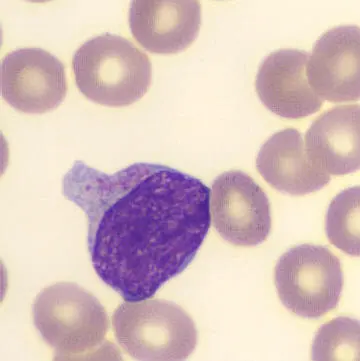
Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) is a haematological malignancy characterised by abnormal clonal expansion of myeloid blasts and impairment of normal haematopoiesis. The impairment of normal haematopoiesis causes clinical sequalae of severe infections, symptomatic anaemia and haemorrhage. Some patients who present primarily with extramedullary disease may have symptoms arising from local compression or organ impairment.

Leave A Comment