Relevant physical signs
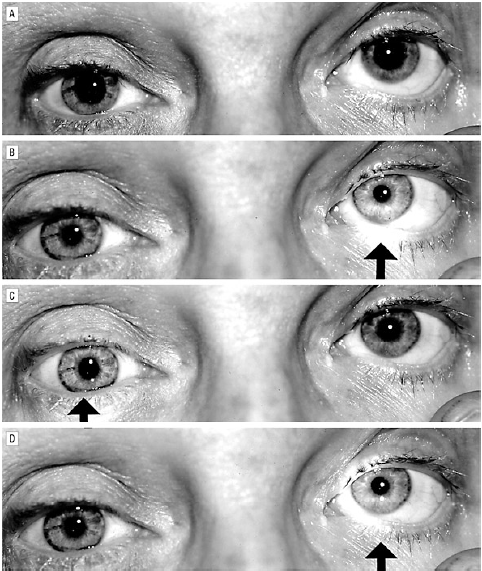
- Testing for an RAPD
- RAPD demonstrates an ipsilateral partially-injured optic nerve
- For a right-sided RAPD:
- At rest, both pupils are of equal size in dim light
- When light is shone into the left eye, both pupils constrict normally
- When the light is swung over to the right side one second later, both pupils dilate, although they remain smaller than at rest.
- When the light is swung back to the left side, both pupils constrict again
- Pupils always remain equal
- RAPD is shown by weaker bilateral pupil constriction in the affected eye compared with the other
- Red desaturation
- Test visual acuity to finger counting
- Hold up a red hat pin an ask the patient what colour it is
- Eye movements
- Internuclear ophthalmoplegia
- Complex ophthalmoplegias
- Nystagmus
- Other cranial nerves
- Jaw jerk (pseudobulbar palsy)
- Look for facial weakness
- Look for pseudobulbar palsy
- Increased gag reflex
- Absent palatal movement
- Spastic tongue (cannot be protruded)
- Cerebellar
- Assess for cerebellar / bulbar / pseudobulbar speech
- Intention tremor / dysmetria
- Dysdiadochokinesis
- Assess gait if possible
- Others
- Pronator drift
Differential diagnosis
- Optic neuropathies
- Optic neuritis
- Multiple sclerosis
- Neuromyelitis optica
- Giant cell arteritis
- Glaucoma
- Traumatic optic nerve injury
- Optic nerve glioma
- Sarcoidosis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Sjögren’s syndrome
- Wegner’s granulomatosis
- Optic neuritis
- Orbital disease
- Thyroid eye disease
- Orbital cellulitis
- Orbital tumour
- Infection
- Cryptococcus
- Lyme disease
- West Nile virus
- Cytomegalovirus
- Toxoplasmosis
- Herpes simplex virus
- Syphilis
- Iatrogenic
- Ethambutol
- Infliximab
- Radiation-induced optic nerve damage
- Leber’s optic neuropathy
- Retinal disease
- Retinal detachment
- Central retinal vein occlusion
- Central retinal artery occlusion
- Severe macular degeneration
Investigations
- Visual evoked potentials
- Consider aquaporin-4 antibodies (neuromyelitis optica)
- Lumbar puncture looking for unpaired oligoclonal bands
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and spinal cord looking for lesions disseminated in space
- Consider temporal artery biopsy
- Consider auto-antibody panel
- Thyroid function tests if clinically-indicated
Management
- See section on Multiple Sclerosis
- For giant cell arteritis: prednisolone 1mg/kg for two weeks, then tail

Leave A Comment