Normal Haematopoiesis
Haematopoiesis is the process by which all blood cells are formed and starts with a pluripotent stem cell. This is a rare cell with a unique self-renewal property which can also differentiate and mature into all cell types.

Haematopoiesis. The haematopoietic stem cell (HPSC) differentiates into common myeloid progenitor (CMP) or common lymphoid progenitor (CLP) cells. CMPs can general all mature myeloid cells while granulocyte-monocyte progenitors (GMPs) or megakaryocyte-erythroid progenitors (MEPs) produce only myeloid/monocytic and megakaryocytic/erythroid lineage cells respectively. B and T lymphocytes and NK cells differentiate from the common lymphoid progenitor (CLP).
Sites of Haematopoiesis
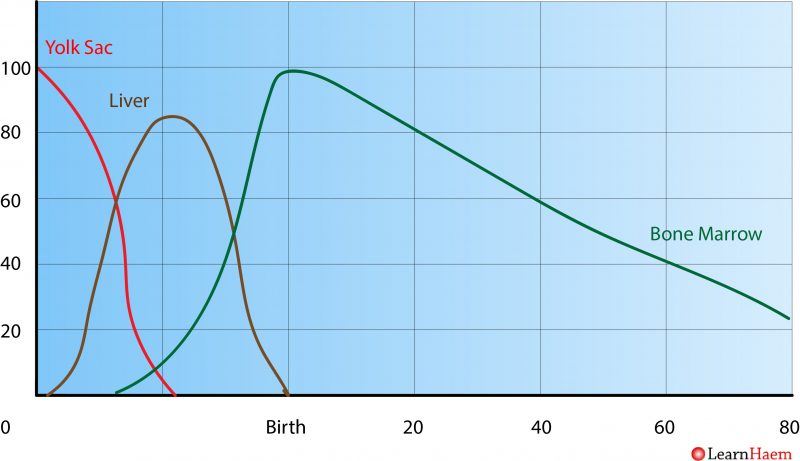
Haematopoiesis starts in the embryonic yolk sac and moves to the foetal liver and spleen after a few weeks (see figure below). The bone marrow then takes over as the main source of new blood cells from 6 months gestation. After birth, active red marrow is gradually replaced by yellow fat marrow so that from age 20, haematopoiesis is concentrated in the axial skeleton and articular ends of the femoral and humerus bones.


very informative and concise
Thank you! Please bear with us as we add more content.
Thanku so much tlfor this kind effort. 💓
It vey useful and easy to understand for the students.Thanks
This is in-depth knowledge simplified indeed. Many thanks for such awesome content
This was such an easy to understand and concise introduction to the topic, thank you so much!
I found this site very helpful for Medical School students like me who wants to learn and appreciate the knowledge . Thank you very much .