Purpose of Test
- Detect antibodies in the serum
- The main application in transfusion medicine is to detect red cell alloantibodies
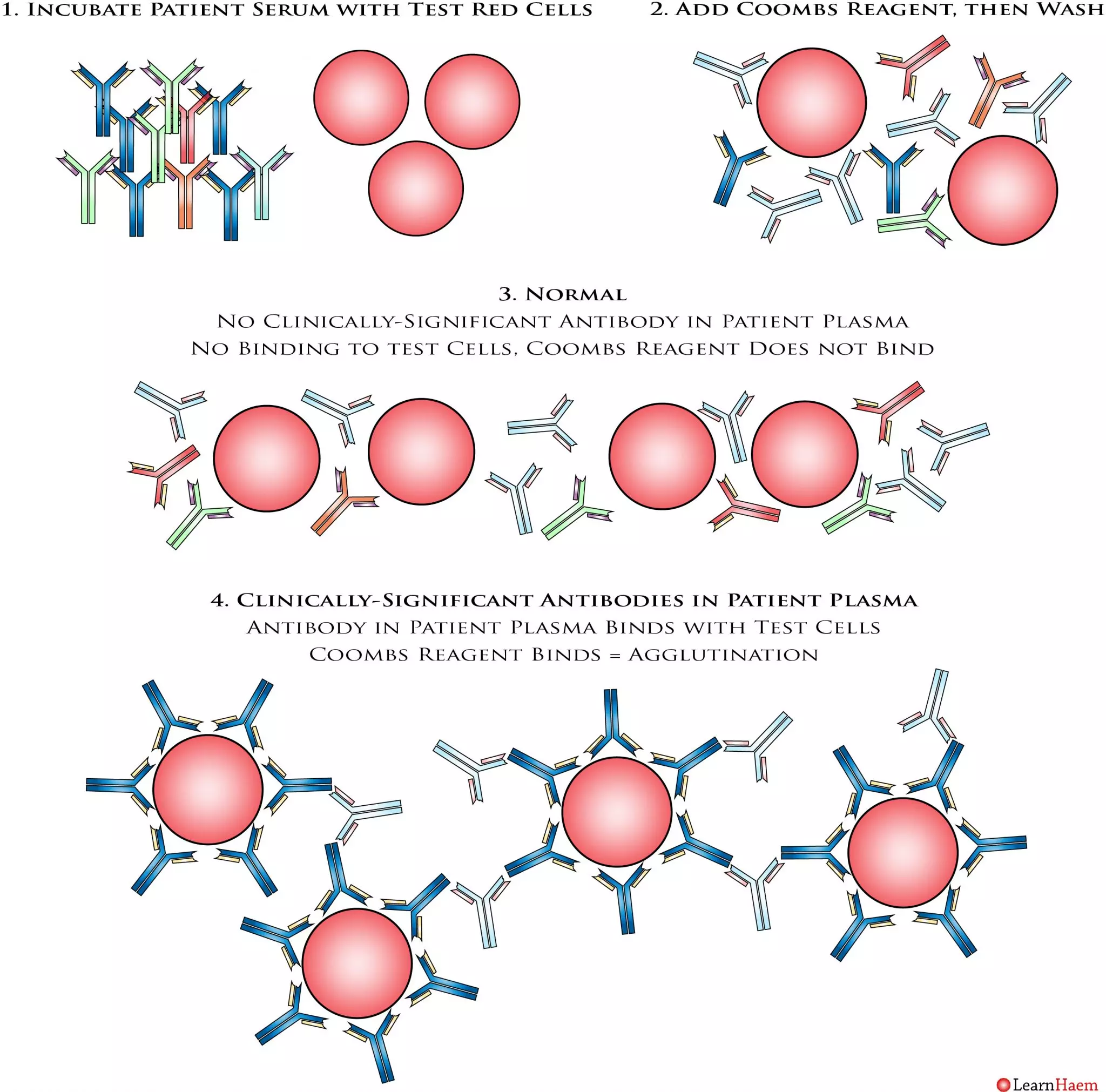
The Indirect Coombs Test Explained

The patient’s serum is incubated with a panel of red cells (test cells) which express a variety of known antigens. After this, the Coombs reagent is added. After allowing the reagents to incubate, the mixture is washed, which removes anything not bound to a red cell surface. In a normal situation, a patient should not have any clinically-significant red cell alloantibodies. Hence, there should be no reaction between the patient’s plasma and the test red cells. In a situation where there is a clinically-significant red cell antibody, the antibody in the patient’s plasma will bind to the test red cells. When the Coombs reagent is added, agglutination occurs, resulting in a positive indirect Coombs test.

Leave A Comment