Diagnostic features
- Scaly plaques, usually in elderly patients
- MF has an indolent disease course, usually over years
- Sezary syndrome is an aggressive disease, which presents with erythroderma, lymphadenopathy and circulating Sezary cells. Criteria:
- Sezary cell count >1000/microlitre
- Expanded CD4+ population leading to CD4:8 ratio >10
- Loss of one or more T cell antigens (often CD7 and CD26)
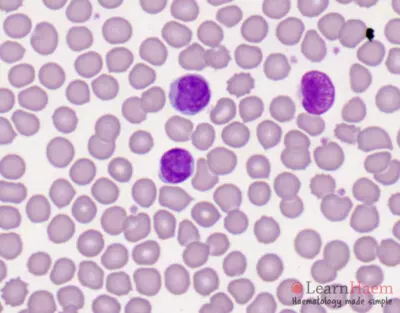
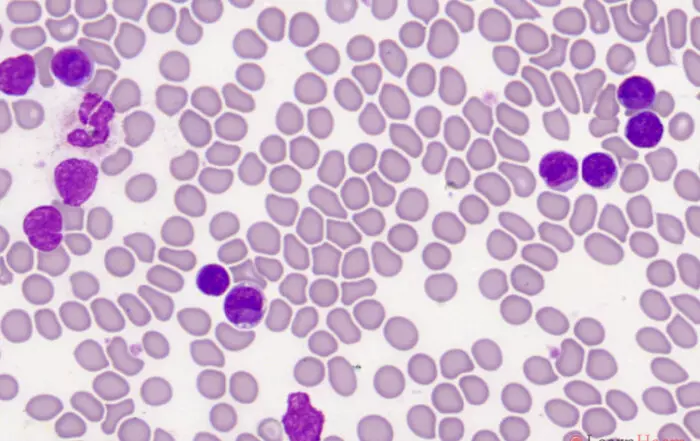
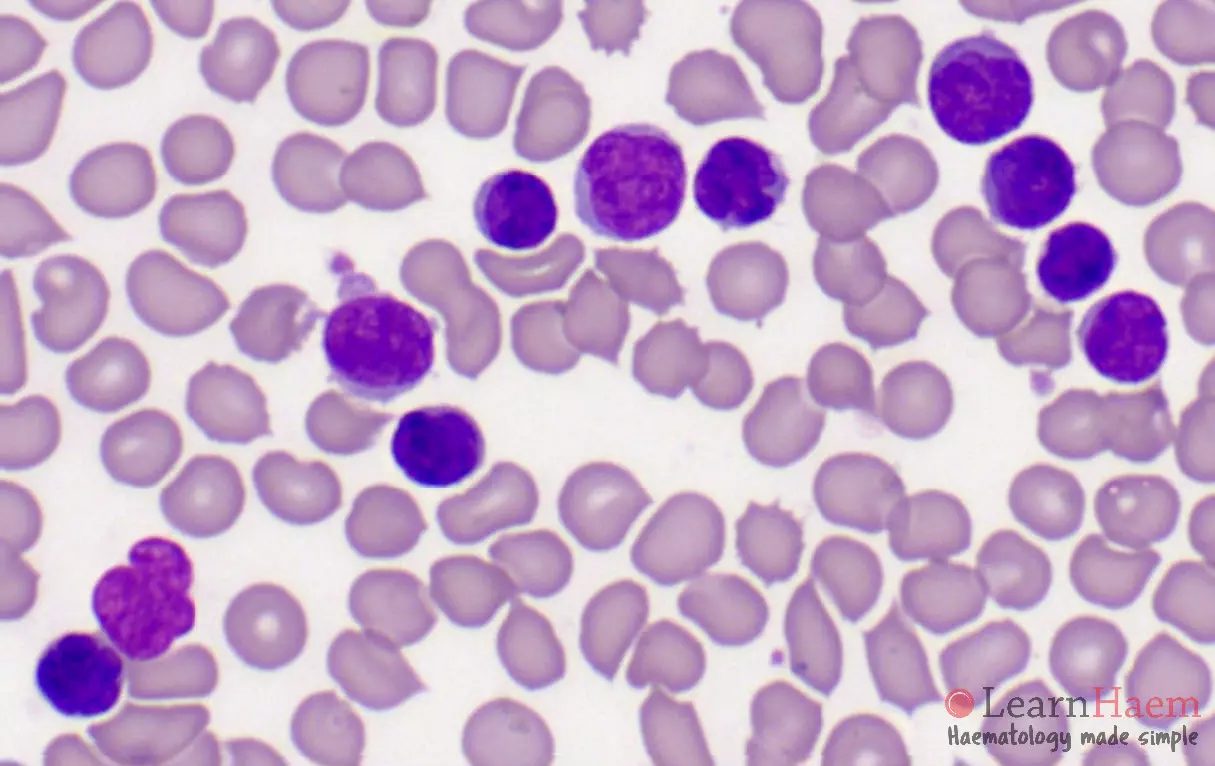
Morphological features
Previous
Next
- Circulating Sezary cells
- Medium-large size
- Convoluted, cerebriform nuclei with tightly intertwined nuclear lobes
- Scanty cytoplasm
- May be vacuolated
- Nuclear groove may be present
- No nucleoli
- May have reactive eosinophilia
Toolbar
Adjustments
Brightness
Contrast
Saturation


0 x
Toolbar
Adjustments
Brightness
Contrast
Saturation


0 x
Toolbar
Adjustments
Brightness
Contrast
Saturation


0 x
Toolbar
Adjustments
Brightness
Contrast
Saturation


0 x
Differential diagnosis
- Hypogranular APML
- Mantle cell lymphoma
- Follicular lymphoma (small cell variant)
Further investigations
- Immunophenotyping: CD3+/4+/8-/7-/26-/PD1+

Leave A Comment